Finding a Job in South Korea as a Foreigner
South Korea offers a dynamic job market for foreigners, with opportunities in industries like education, technology, and business. Whether you're seeking a position in a multinational company or a local firm, understanding South Korea visa requirements, job search platforms, and workplace culture is essential. This guide will help you navigate the process of finding a job in South Korea as a foreigner, from identifying opportunities to securing the right visa.

Understanding Work Visa Requirements
To work legally in South Korea, you need the correct visa. The type of visa you apply for depends on your job type, nationality, and qualifications.
Common Work Visas for Foreigners
|
Visa Type |
Purpose |
Who It’s For |
Validity |
|
E-2 Visa (English Teaching) |
Teaching English in schools or private academies (hagwons) |
Native English speakers with a bachelor’s degree |
1 year (renewable) |
|
E-7 Visa (Skilled Workers) |
Teaching English in schools or private academies (hagwons) |
Skilled professionals with relevant qualifications |
Varies |
|
D-8 Visa (Investment & Business) |
Entrepreneurs, business investors, and employees of foreign companies |
Business owners and foreign company transfers |
Varies |
|
D-8 Visa (Investment & Business) |
Entrepreneurs, business investors, and employees of foreign companies |
Business owners and foreign company transfers |
Varies |
|
H-1 Visa (Working Holiday) |
Entrepreneurs, business investors, and employees of foreign companies |
Young adults from eligible countries |
1 year (not renewable) |
|
D-10 Visa (Job-Seeking Visa) |
Allows job searching while in South Korea |
Foreigners looking for work in Korea |
6 months (extendable) |
Finding Job Opportunities in South Korea
South Korea offers diverse job opportunities in fields like teaching, IT, finance, and entertainment. To find the right job, candidates should explore online job portals, industry-specific boards, recruitment agencies, company career pages, and networking events.
- Job Search Websites: Online portals list job openings across various industries, with some tailored for foreigners and others requiring basic Korean proficiency.
- Industry-Specific Job Boards: Certain fields, such as IT and finance, have dedicated platforms featuring specialized roles and salary details.
- Recruitment Agencies: These agencies connect job seekers with employers, particularly in multinational companies and specialized sectors, while also offering career support.
- Company Career Pages: Many businesses post job openings on their websites, allowing candidates to apply directly and stay updated on hiring trends.
- Networking & Events: Industry conferences, job fairs, and professional meetups help build connections, as many positions are filled through referrals.
Preparing Your Application (Resume & Interview)
A well-prepared job application is essential for securing a position in South Korea. Employers expect a structured resume, a compelling cover letter, and strong interview performance. Understanding local hiring preferences and adapting your application to meet Korean standards can significantly improve your chances of success.
- Korean-Style Resume: Most employers prefer a structured format that includes a passport-sized photo, personal details, and a chronological work history. Relevant skills and certifications should also be highlighted.
- Cover Letter: A concise, professional letter explaining your motivation and how your skills match the company’s needs. Writing in Korean, if possible, can be an advantage.
- Interview Process: Most interviews involve multiple rounds, from HR to senior management. Basic Korean proficiency is beneficial, and employers value teamwork, respect for hierarchy, and a strong work ethic.
Work Culture & Salary Expectations

Understanding workplace culture and salary expectations is crucial when seeking employment in South Korea. The country’s corporate environment emphasizes hierarchy, respect, and group harmony. Salaries vary depending on the industry, experience, and job role, with competitive compensation packages offered in specialized fields.
- South Korean Work Culture: Offices follow a hierarchical structure where titles and honorifics are important. While long hours are common, efforts to improve work-life balance are increasing. Company dinners (hoesik) are key to workplace relationships.
- Salary Expectations: Compensation depends on industry and experience. Teaching offers stable income with benefits, while IT, engineering, and finance provide higher salaries. Marketing and sales roles often include performance-based incentives, and many jobs offer additional perks like bonuses and housing stipends
Final Tips for Success in Finding a Job in South Korea
Securing a job and adjusting to life in South Korea requires preparation, adaptability, and persistence. Here are some key tips to improve your chances of success:
- Learn Basic Korean: Even a conversational level of Korean can make a significant difference in job opportunities and workplace interactions.
- Adapt to Korean Work Culture: Understanding workplace hierarchy, etiquette, and professional expectations helps in building strong relationships with colleagues and employers.
- Be Persistent: The job search process can take time, so staying patient, proactive, and open to different opportunities is crucial.
- Use Multiple Job Search Strategies: A combination of job portals, networking, company career pages, and recruitment agencies increases your chances of finding the right position.
Becoming Self-Employed in South Korea

Becoming self-employed in South Korea requires the right visa, business registration, financial planning, and an understanding of local work culture. Whether freelancing or starting a business, here are the key steps to follow:
- Visa and Legal Requirements: To work legally, you need a South Korea visa that allows self-employment, such as the D-8 (Business Investment Visa) for entrepreneurs or the F-series visas for long-term residents. Consulting immigration experts can help determine the best option.
- Business Registration: All self-employed individuals must register with the National Tax Service (NTS). This includes obtaining a Business Registration Certificate and securing any necessary licenses based on the type of business.
- Taxation and Financial Considerations: Self-employed professionals must handle their own taxes, including income tax, VAT (if applicable), and contributions to national pension and health insurance. Keeping organized financial records or hiring an accountant can help ensure compliance.
- Setting Up a Business Bank Account: A local bank account is necessary for managing business transactions. To open one, you typically need a valid visa, Alien Registration Card (ARC), and business registration documents.
- Finding Clients and Marketing Your Business: Networking is essential in South Korea. Using online platforms, attending business events, and leveraging digital marketing can help attract clients and grow your business.
- Workspaces and Business Operations: Depending on your needs, you can work from home, rent a co-working space, or lease a commercial office. Co-working spaces are a flexible and cost-effective option for freelancers and startups.
- Understanding South Korea’s Business Culture: Building strong professional relationships requires understanding hierarchy, respecting business etiquette, and maintaining reliability. Establishing trust and professionalism will help you succeed in the market.
How to Apply for an Alien Registration Card (ARC) in South Korea
In South Korea, foreign residents staying for more than 90 days must obtain an Alien Registration Card (ARC). This card includes a unique Foreign Registration Number, which functions similarly to a social security number. It is essential for opening bank accounts, obtaining a mobile phone, and accessing public services.
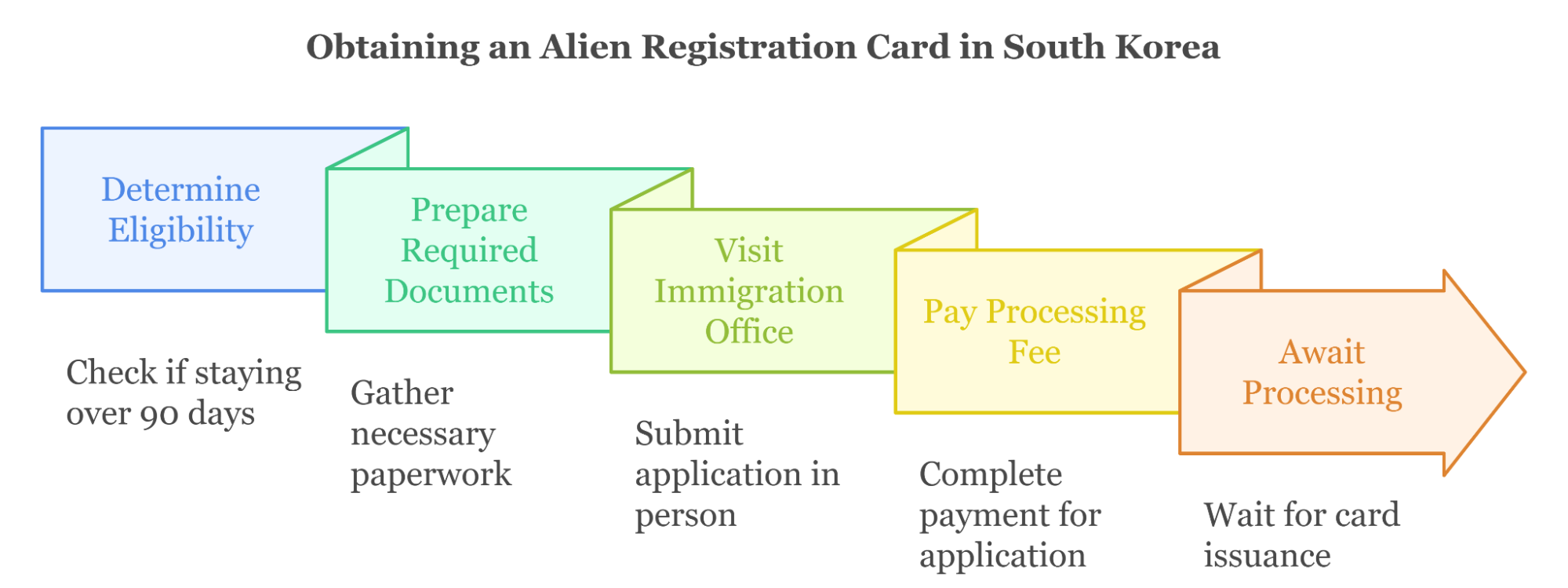
Application Process for the Alien Registration Card (ARC)
- Determine Eligibility:Any foreigner staying in South Korea for over 90 days must apply for an ARC within 90 days of arrival.
- Prepare Required Documents
- Completed Application Form – Available at local immigration offices or their official websites.
- Passport – Original passport with a valid visa.
- Passport-Sized Photograph – A recent color photo (3.5 x 4.5 cm) with a white background.
- Proof of Residence – Housing contract or utility bill.
- Additional Documents – Employment contracts, enrollment certificates, or other documents, depending on visa type.
- Visit the Immigration Office:Submit your application in person at the immigration office for your area of residence. Booking an appointment in advance is recommended.
- Pay the Processing Fee: A small fee is required when submitting your application.
- Await Processing:The ARC is usually processed within 2-4 weeks. You can collect it in person or have it mailed to your address.
Guide to Relocating and Settling in South Korea

Moving to South Korea involves more than just securing a job—it requires careful planning for housing, banking, communication, healthcare, and daily expenses. Understanding these aspects can help ease your transition and ensure a smooth relocation.
-
Housing Options
Housing in South Korea varies based on budget, location, and employer benefits. Some companies provide housing or a stipend, reducing accommodation costs. Budget-friendly options like goshiwon (small, single rooms) are ideal for short-term stays, while one-room apartments are popular among professionals seeking privacy and convenience.
-
Banking & SIM Cards
Opening a bank account in South Korea requires an Alien Registration Card (ARC). Major banks offer various services tailored for foreigners, making banking more accessible. For mobile connectivity, South Korea has reliable providers offering prepaid and contract-based plans to suit different needs.
-
Health Insurance & Living Costs
South Korea’s National Health Insurance (NHIS) provides medical coverage, and employers typically enroll their staff in the program. The cost of living depends on the city, with Seoul being the most expensive, while smaller cities offer more affordable living expenses. Budgeting wisely ensures a comfortable lifestyle.
Tips for Success in Working in South Korea
Succeeding in South Korea’s workplace requires adaptability, professionalism, and cultural awareness. Understanding the work culture, networking, and continuous learning can help you thrive. Here are key tips to ensure a smooth and successful career in South Korea.
- Learn Basic Korean – Even if your job doesn’t require fluency, knowing basic Korean can help with daily interactions and workplace communication.
- Understand Workplace Culture – Respect for hierarchy, teamwork, and professionalism are highly valued. Observe and follow company etiquette.
- Adapt to the Work Environment – Be prepared for long working hours and a structured work culture. Maintaining a positive attitude and strong work ethic will help you integrate smoothly.
- Network Actively – Building professional relationships through networking events and industry gatherings can open doors to better opportunities.
- Be Punctual and Professional – Arriving early and being well-prepared for meetings shows commitment and respect, which is highly appreciated in South Korea.
- Embrace Company Social Culture – Participating in company dinners (hoesik) and group activities helps build relationships with colleagues and supervisors.
- Stay Open-Minded and Flexible – Work expectations and processes may differ from your home country. Being adaptable will help you succeed.
- Know Your Rights – Familiarize yourself with labor laws, contract terms, and benefits to ensure fair treatment at work.
- Take Care of Your Health – South Korea offers excellent healthcare, so make sure you’re covered under the National Health Insurance (NHIS) and maintain a good work-life balance.
- Keep Learning and Upskilling – Continuous improvement, whether through Korean language studies or job-related certifications, can enhance your career prospects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need to speak Korean to work in South Korea?
While some jobs, especially in multinational companies and English teaching, don’t require fluency, knowing basic Korean (TOPIK Level 2 or higher) improves job prospects and workplace communication.
What visa do I need to work in South Korea?
The required visa depends on the job. The E-2 visa is for English teachers, the E-7 visa is for skilled professionals, and the D-8 visa is for investors or business owners.
Is it difficult for foreigners to find jobs in South Korea?
It depends on the industry. Teaching, IT, and engineering have high demand for foreign workers, while other fields may require fluent Korean and strong local networks.
What is the typical work culture like in South Korea?
The workplace emphasizes hierarchy, teamwork, and long hours, though work-life balance is gradually improving. Company dinners (hoesik) are common for team bonding.
How can I increase my chances of getting hired?
Tailor your resume to the Korean format, learn basic Korean, network through job fairs and LinkedIn, and apply through multiple job search platforms, including company career pages.
Content Disclaimer: Although this information was last updated in February 2025, we recommend verifying with the appropriate agencies, embassies, and airlines to ensure complete accuracy regarding your travel plans.
2 Comments
Muhammad Sharib 31 Jul, 2025
My name is Sharib. I am from Pakistan. My qualification is FA . I need work.
Muhammad Sharib 31 Jul, 2025
My name is Sharib. I am from Pakistan. My qualification is FA . I need work.